Get More from Imagery Using 30 New Features Released to Geomatica Banff

PCI Geomatics is the developer of Geomatica, a leading software remote sensing, digital photogrammetry, geospatial analysis, map production, mosaicking and more.
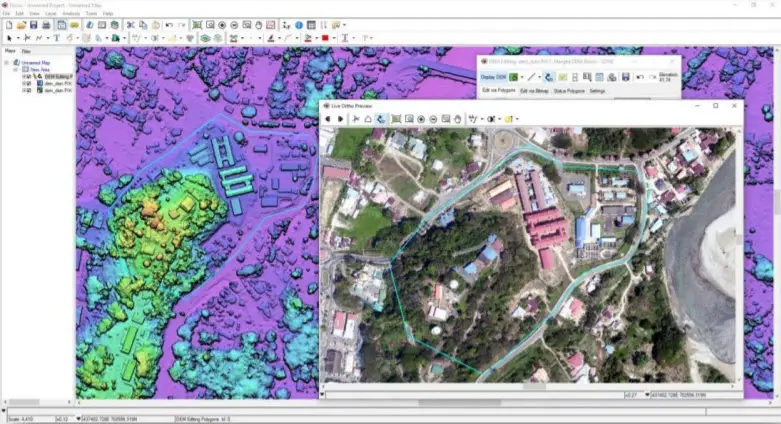
Geomatica Banff introduces automation for object-based image analysis. Automation is available in Focus from the Object Analyst or can be implemented as a chained workflow with individual algorithms (and Python). Building training data can be from multiple locations and deployed to classify and extract features of temporally overlapping imagery or data sets covering various geographic areas. Now just train data sets once and classify consistently over-and-over again.

Recently, PCI Geomatics has thrilled the market with the release of over 30 new capabilities/features and enhancements to best of breed photogrammetry and remote sensing solution, Geomatica Banff.
The 30 New feature highlights in Geomatica Banff can be summed up as –
- Complete end-to-end workflow for UAV imagery,
- New Random Forest machine learning classifier for object analysis
- 19 new or enhanced algorithms
- 5 new or enhanced sensor support
- Support for CentOS 8
- Bug fixes
Let’s look at some feature in detail
1. Complete UAV Workflow – with new end-to-end UAV workflow and self-camera calibration feature, user can create high-quality 3D models and ortho-mosaics faster and at a lower cost.
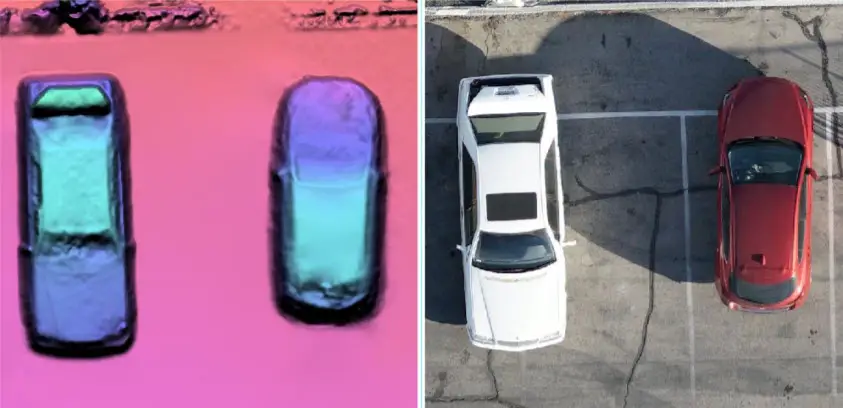

2. New Random Forest ML Algorithm – this feature allows to consistently extract accurate information from your UAV, satellite, aerial and SAR imagery using our new random forest classifier, called Random Trees.
3. New Functions
- APUNDISTORT: Resamples raw imagery to compensate for distortions in aerial photos, reducing the effects of distortion caused by camera lens, atmospheric refraction, earth curvature or other unpredictable errors. Distortion corrected images can be used directly in stereo measurement to improve epipolar generation and the quality of the subsequent DEM.
- MIRROR: Mirror images along the vertical or horizontal axes, maintaining the location of GCPs in the process. MIRROR can be applied to airborne radar or multispectral data, enabling the inversion of descending images to ascending images, or to convert left-looking imagery to right-looking imagery.
- OARTCLASS: Uses the Random Trees (RT) algorithm to run a supervised classification based on an RT training model you specify. Technology-based on the Random Forest algorithm (Breiman (2001).
- OARTTRAIN: Uses a set of object samples, stored in a segmentation-attribute table, to develop a predictive model by creating a set of random decision-trees and by taking the majority vote for the predicted class. Technology-based on the Random Forest algorithm (Breiman (2001).
- SELFCAL: Refines tie points and ground control points with camera self-calibration. Note: Camera self-calibration is required when no external camera calibration has been provided, or if the provided external camera calibration is not accurate.
- TIEIMAGE: Find TPs and optionally GCPs using Fast Fournier Transform (FFT) phase matching. FFT methods produce a more uniform grid of points and are appropriate for data sets with good initial estimates of exterior orientation. When used in addition to FBM, TIEIMAGE is a powerful method for determining the exterior orientation of UAV imagery.
- VDISSOLVE: Automatically dissolve the boundaries between vector shapes from an input segment. All attribute information from the input shapes is maintained in the dissolved shape, enabling the robust and easy calculation of dissolved shape attributes.
4. New Sensor Support
- ICEYE: Support added for SLC datasets. ICEYE is a SAR Satellite constellation capable of reliably imaging the entire Earth every 1-3 hours
- Orbita: Support added for Level 1B OHS-2A, OHS-2C, and OHS-2D datasets. Orbita is a hyperspectral satellite constellation with a spectral resolution of 2.5nm, and a ground sampling distance of 10m
5. Updated Sensor Support
- Landsat ARD: Updated the default RGB band combination to display ARD products as NIR-SWIR-RGB, improving the ease of using Landsat ARD data for spectral calibration. Addition of support for Surface Temperature (ST) products
- PALSAR-2: Full support for the RADARSAT Constellation Mission GeoCoded Detected or Complex products
- Sentinel-1: Metadata updates to help improve the overall InSAR process for TOPS data
See all the new Geomatica features and enhancements from the June 9, 2020 release