SpatialCover Tree Canopy Minnesota Overview
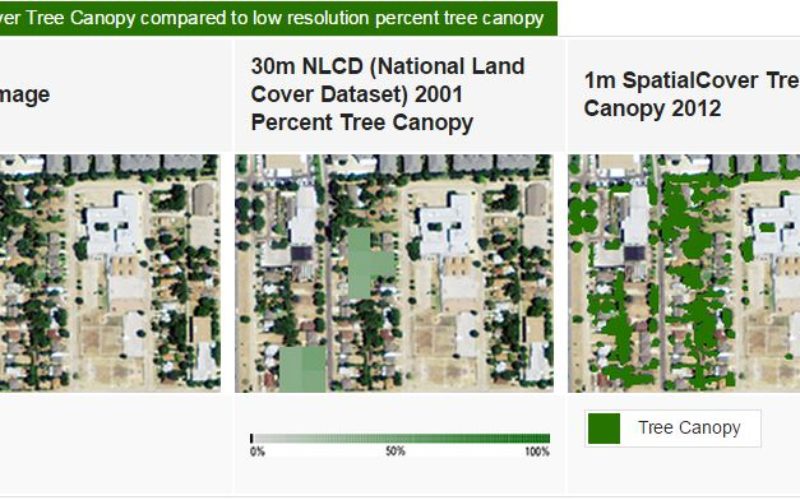
EarthDefine has created a high resolution tree mapping datasets for Minnesota’s tree in unprecedented detail. The high resolution seamless tree canopy dataset for Minnesota have 98% accuracy and 30 times the resolution of existing state level datasets for Minnesota.
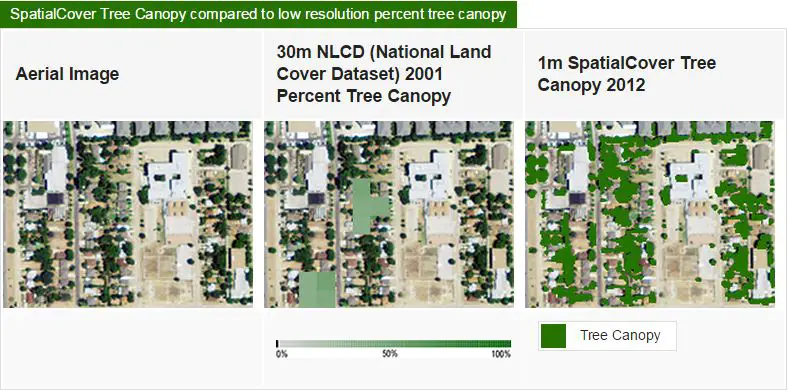
SpatialCover Tree Canopy is a product by EarthDefine, with 1 meter tree canopy data product that provides baseline tree cover information in multiple formats to support improved management of tree resources and carbon quantification. SpatialCover Tree Canopy is derived from LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data where available. LIDAR technology enables accurate measurement of elevation for different ground surface types based on the light pulses reflected from the earth. Satellite Images are is used as the primary data source in areas where there is no usable LiDAR and sometime in combination with LiDAR point clouds.
The SpatialCover Tree Canopy Minnesota dataset supports numerous applications for urban planning, forest inventory and ecosystem analysis. Such as:
- mapping actual and potential tree canopy in urban communities through Urban Tree Canopy (UTC) assessments
- modeling of tree services like air and water pollution mitigation
- measuring carbon storage and sequestration
- wildfire modeling
- assessing residential property values
- modeling wildlife movement
- creating and analyzing forest inventory
- measuring agroforestry resources in rural landscapes
Credit: EarthDefine
EarthDefine has previously released high-resolution tree canopy datasets that provide statewide coverage for Indiana and California.
The Approach
A Digital Surface Model (DSM) was created from first returns of the LIDAR point cloud data and bare earth elevations were removed from the DSM to derive an above ground surface model. Buildings and tree canopy were differentiated in the above ground surface model through an expert rule based classification system. Morphological filtering was used to fill small data gaps and improve the cartographic quality of the final product. For counties where the LIDAR data was not suitable as a primary data source for tree cover classification, 4 band color NAIP (National Agriculture Imagery Program) imagery was classified using a Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis (GEOBIA) workflow and combined with the LIDAR data to produce the tree canopy layer.