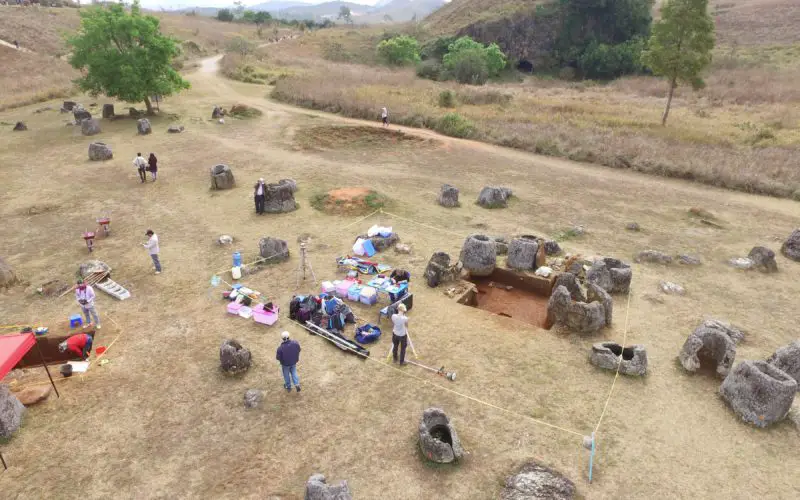
Archaeologists at The Australian National University (ANU) and Monash University are conducting a trial of new technology to build a 3D virtual-reality map of one of Asia’s most mysterious sites – the Plain of Jars in Laos.
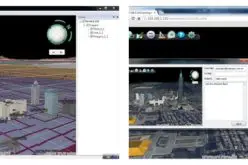
Researcher Dr Dougald O’Reilly from the ANU School of Archaeology and Anthropology said the technology, known as CAVE2™ and based out of Monash University, uses drone footage to create a virtual replica of archaeology dig sites.
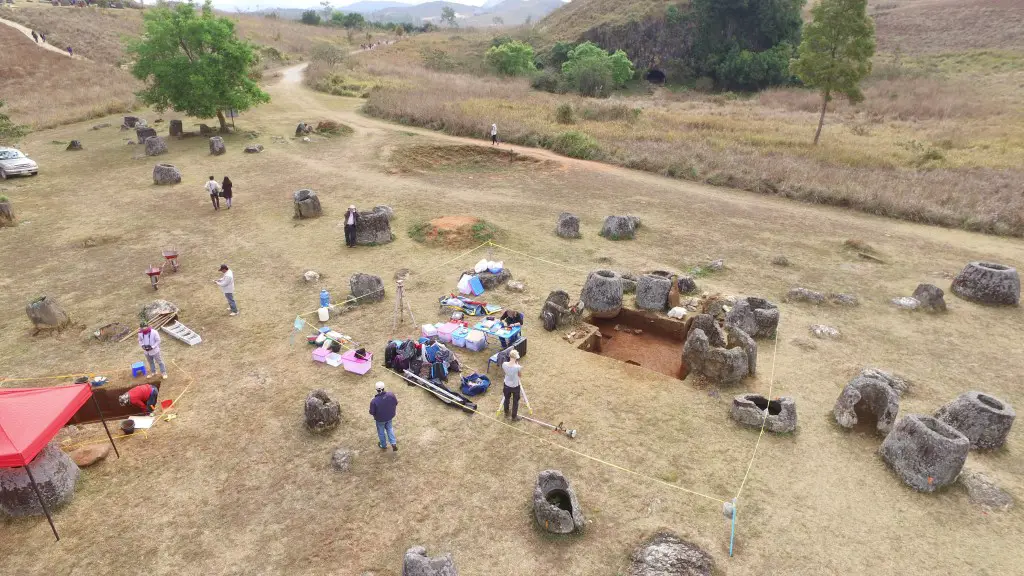

Researchers Used a Drone To Take Overhead Photos.
Credit: ANU
“On top of mapping the three dig sites, we are doing the entire Plain of Jars landscape,” Dr O’Reilly said.
“A drone captures a set of 3D images every 10 centimetres and this data is put into a digital mould.
“You put on a headset and the virtual model feels like you’re standing and walking around the site. As you move around the image moves as if you are at the location.”
Ground penetrating radar was also used to identify a burial which researchers then excavated. That data was also fed into CAVE2™ to create a 3D underground view.
Dr O’Reilly said it was possible for the technology to be adapted to smartphones, or to do 3D printing of the digital models.
“It provides easy access to remote faraway places. Theoretically you could use the headset with your phone to visit a 3D map of any location,” he said.
“You could print a life-sized version of any CAVE2™ model. You could use them in museums rather than disrupting the archeologically record by moving artefacts.”
Dr O’Reilly said the technology could be a great benefit to the field of archaeology.
“It allows you to revisit the site. Even right now I’m using it to look at the positioning of some of the materials I’m having radio-carbon dated,” he said.
“In terms of heritage preservation it’s a useful tool. If you want to monitor the change in heritage sites through time you have that data.”
The Plain of Jars was chosen as a test site for CAVE2™ due to the current application to have the site listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
The Plain of Jars dig project in central Laos is the first major archaeological dig at the site since the 1930s. The landscape features ancient carved stone jars up to three metres tall, their purpose remains a mystery.
The site features a number of the large stone jars for which the site is named, as well as a big sandstone disk and large quartz stones.
The project was jointly led by Dr O’Reilly and Dr Louise Shewan, Monash University.
Dr Shewan said the technology will become useful for investigating sites that are not accessible for traditional archaeological methods, due to issues such as unexploded land mines.
“Of the over 80 known jar sites in Laos, only seven have been cleared of explosives,” she said.
Source: AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY